A mathematical similarity between gravity and electromagnetism has long been noted and commented upon. There are also qualitative analogies that are occasionally mentioned but beyond noting the fact that the gravitational effect around a a gravitating body falls off at the same 1/r2 rate as the density of the electromagnetic radiation being emitted by the body, little thought is given to this rather striking overall correlation. Coupled with the observation that light moving through a gravitational field behaves as if it were traversing a medium with a density gradient, there would seem to be at least a strong indication of a causal relation between gravitational effects and the electromagnetic field (EMF) especially since a gravitational field is only posited, not observed
It will argued here that all gravitational effects can be attributed to the interaction between matter and electromagnetic fields. First, two definitions:
- the ACER (Ambient Cosmic Electromagnetic Radiation} that pervades the Cosmos. This is the cosmological scale field that constitutes The Spectrum of the Universe as described in the document of the same name. This radiation does not have a density gradient but is approximately uniform in distribution around any free-standing body.
- the ERDG (Electromagnetic Radiation Density Gradient) which is the aggregate EMF of all the electromagnetic radiation being emitted omnidirectionally by a radiating body. The strength of that field falls off as 1/r² and therefore it has a density gradient
The Deflection of Light in a Gravitational Field
The EMRG comprises the medium through which the ACER (all external radiation)travels in the vicinity of a radiating/gravitating body. The ERDG is a transparent medium with a density gradient. Light passing through a “gravitational” field behaves as if it were passing through a medium with a density gradient. The ERDG fully accounts for the “gravitational” effect of the curvature of incident light — without invoking an otherwise invisible gravitational field. Essentially the ERDG constitutes a particular type of EMF that causes the effect traditionally attributed to an undetected gravitational field.
Gravitational Attraction
Initially let us consider the isolated case of one star, ignoring for the moment any nearby stellar neighbors. The star in this case has surrounding it both the omnidirectionally sourced ACER and its own locally self-produced ERDG. The ACER that falls on the star directly is absorbed and eventually reemitted as part of the ERDG. There is an additional inflow of radiation from the ACER that can be attributed to the ERDG curving the ACER passing closest to the star onto the surface.
All of this radiational inflow is omnidirectional onto the surface of the star. In a sense the inflow attributable to curvature can be thought of as a “pulling on the nearby ACER but as it is a “pulling” in all directions there is no net effect on the star’s motion through the ACER. The ACER is essentially an inertial medium. Since the ACER is being curved by the ERDG of the star it is reasonable to think of the ERDG as the gravitating medium of the star. The curvature of passing radiation in the vicinity of a gravitating medium is an observed fact predicted by General Relativity but it is also predicted and observed behavior for light passing through any transparent medium with a density gradient
Now we introduce a small, but not infinitesimal, nearby test particle, a planetary object the size of the Earth, with some velocity relative to the star that is not significant with respect to Relativity Theory. Let us also assume that the initial trajectory is toward but not directly at the star. This test body will interact with the ACER that surrounds it in exactly the same way that the star does, with the exception being that the planet is only passively reradiating the radiation from the star that falls upon it – it is a passive not active emitter of electromagnetic radiation. Consequently the radiation density at the planet’s surface will be <<< than the radiation density at the surface of the star and the “gravitational effect” of the planet on the star-planet system will be much weaker.
As the planet draws closer to the star two simultaneously acting effects are taking place. Along the line that joins their centers of mass over an area that is defined by the projection of the planet’s shadow, the star will be curving the nearby passing ACER but no direct inflow will be taking place in that shadow region only a “pulling in” of the passing ACER that lies between the two bodies. A similar but smaller inflow is taking place over the surface of the planet facing the star.
At the same time the planet is passing through the star’s ERDG, with the surface of the planet closest to the star experiencing a stronger “gravitational effect”. That effect is directly attributable to the ERDG – the radiation density from the star is higher on the closer side of the planet. The primary higher density effect is that physical processes slow down in the denser radiation.
The result of the higher density will be the same as it is in any medium with a density gradient – among other things it will slow the passage of the nearer surface through the ERDG medium producing a curvature of the planet’s path while also inducing a rotation. The curved path of the planet is analogous to the curved path of light being caused by a slowing of light in the denser portion closer to the surface of the star. This behavior is typical in mediums with a density gradient. Gravitational attraction then is entirely explicable as an interaction effect between matter and an EMF with a density gradient (ERDG).
Galaxy Clusters
Gravitational lensing around a galaxy cluster requires considerable amounts of undetectable Dark Matter to “fit” the observations (of gravitational lensing) to the standard model. The excess observed curvature implied relative to calculations based on the mass distribution can be attributed to the fact that the x-ray hot plasma that constitutes up to 90% of a cluster’s mass has a higher radiation output than an equivalent stellar mass would produce. That excess high energy radiation will produce a stronger “gravitational” effect than the observed mass alone would predict using the standard gravitational models that correlate gravitational effects with mass density rather than radiation density.
This higher radiational output is due to the diffuse nature of of the cluster gas which is radiating outward from within its entire volume whereas a star is only radiating from its surface area; effectively the x-ray hot gas has a much lower Mass/EMR ratio than a star or galaxy.
This x-ray hot gas constitutes 90% of the cluster’s mass and produces a large excess of high density, high frequency radiation. And that radiation tracks the “gravitational” effects. That’s what’s there. What’s not there is Dark Matter. If gravitational effects are attributable to the density of the cluster’s EMF rather than the unobserved mass-dependent “gravitational” field, the mass discrepancy problem evaporates and with it the need for Dark Matter. Mercifully.
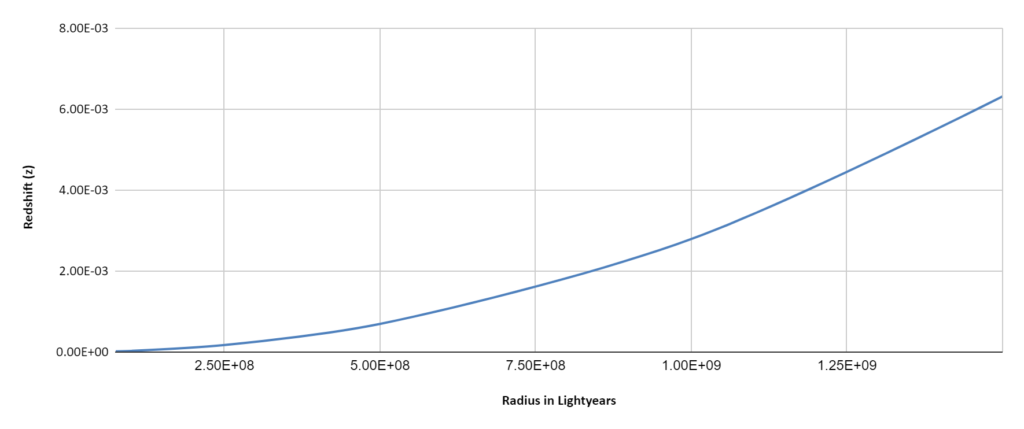
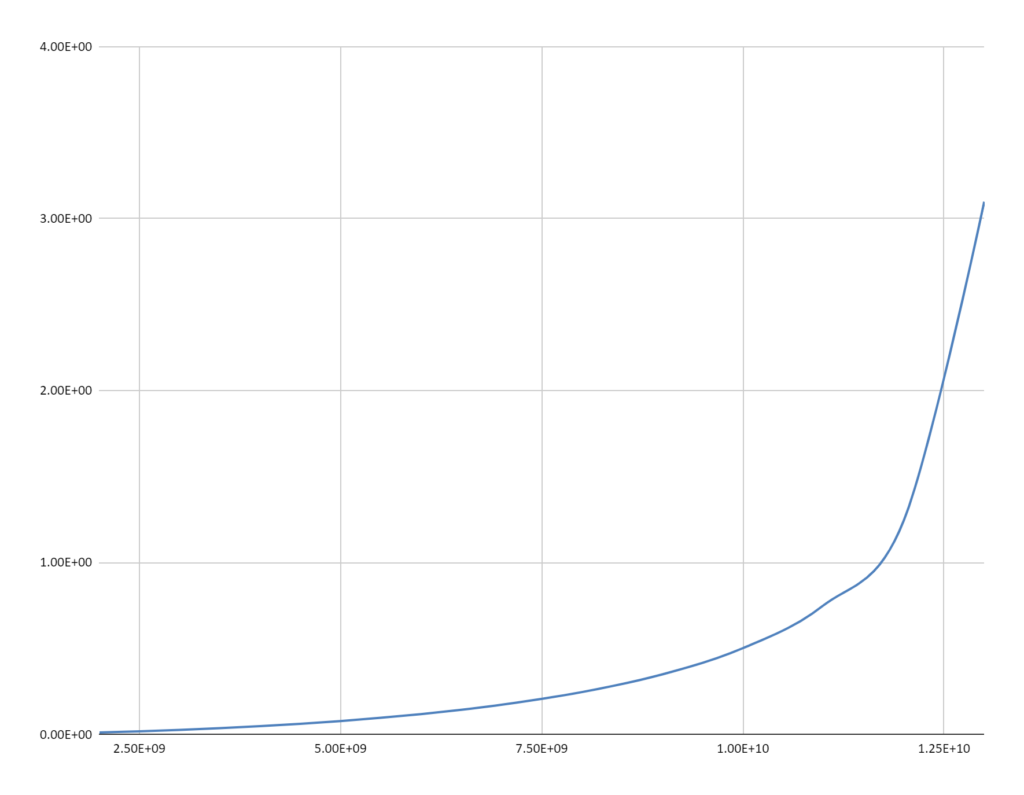
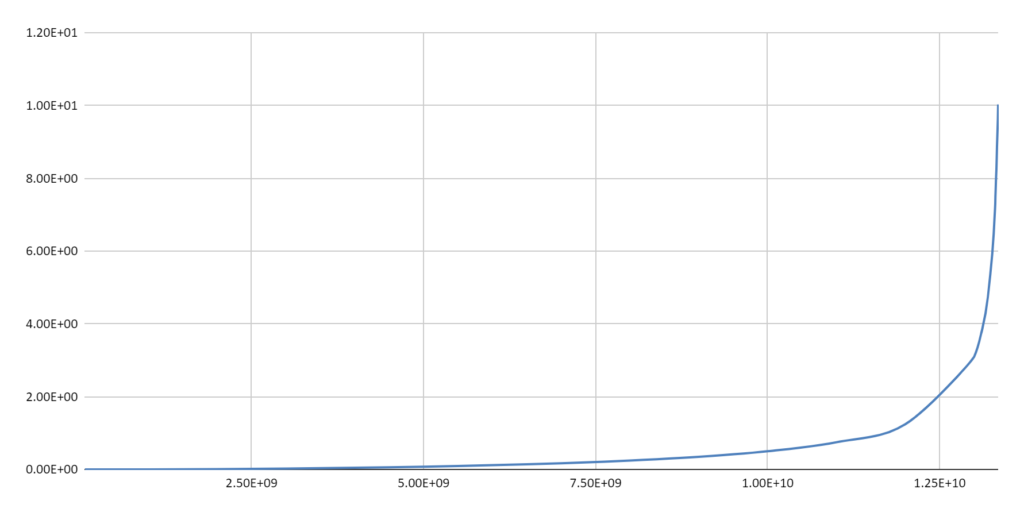
The Cosmological Redshift
It is a demonstrable fact that the General Relativity based math (Schwarzschild solution) that describes gravitational redshift can also be used to calculate the cosmological redshift for an Expanding Spherical Wavefront (ESW) of electromagnetic radiation. The resulting redshift resembles the cosmological redshift of the standard model which uses a different GR solution (FLRW) describing an Expanding Universe. See: Gravitational Redshift & Expanding Spherical Wavefronts
The mathematics involved here is not satisfactory because the Schwarzschild solution does not take into account the variation of light speed in a gravitational field. However, the qualitative picture presented, of an ESW losing energy as it is gradually absorbed by its encounters with galaxies and other intervening matter, demonstrates once again that an effect that can be described with standard gravitational math can be understood as arising from the direct interaction of Matter and electromagnetic fields.
The ACER is the aggregate of all the ESWs streaming through the Cosmos. A galaxy’s ERDG becomes a continuous outflow of ESWs on cosmological scales as the density gradient becomes negligible.
Coda
It is certainly fair to say that none of the foregoing constitutes “proof” that Matter-EMF interactions are responsible for all the various observed effects attributed to gravity. However science does not deal in “proofs” – those lie in the realm of mathematics and mathematics is not science. Science and physics deal in empirical evidence and the facts as presented here constitute, at minimum, strong evidence that the observed gravitational effects are correlated with observed Matter-EMF interactions.
As mentioned these correlations are not unknown and have been remarked upon elsewhere (excluding the ESW section) but that is all that has transpired. No serious research, either empirical or theoretical, has been conducted to determine if that correlation indicates a causal relation. Yet, MTP offers no explanation for the physical cause of gravity at all. Why then, this peculiar incuriosity? It seems attributable to the scientific academy having some legacy math that has been handed down for a century or more (if you count Newtonian gravity) and though neither the Newtonian nor Einsteinian gravitational models work on the scale of galaxies and galaxy clusters there exists a dogmatic belief, despite this obvious evidence to the contrary, that those models constitute Universal Laws.
The irrational result is that modern theoretical physicists appear to believe they know everything there is to know about gravity because they have some math (that doesn’t work well) and therefore there is no reason to do any research into what they do not know (the cause of gravity) because if it was important someone would have taught them about it in graduate school. Something like that. There really is no sensible explanation for the situation.